What Happens to Genetic Material During Cell Division?
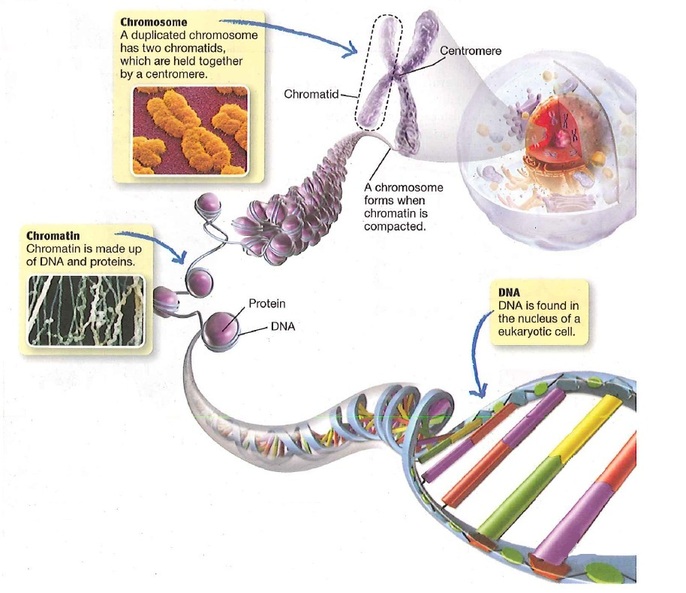
The genetic material in cells is called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). A DNA molecule contains the information that determines the traits that a living thing inherits and needs to live. It contains instructions for an organism's growth, development, and activities. In eukaryotes, DNA is found in the nucleus.
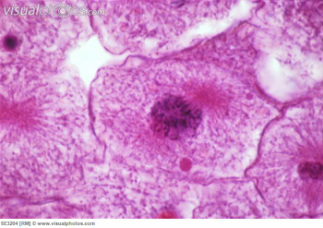
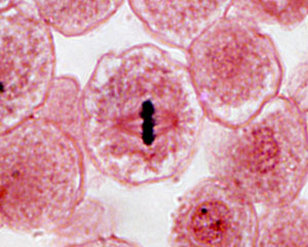
During most of a cell's life cycle, DNA, along with proteins, is a mass of loose strands called chromatin (KROH-muh-tin). Before cell divion, DNA is duplicated, or copied. Then, in an early stage of cell division, the chromatin is compacted into visible structures called chromosomes (KROH-muh-sohmz). A duplicated chromosomes consists of two identical structures called chromatid (KROH-muh-tidz). The chromatids are held together by a centromere (SEN-truh-mir).
During most of a cell's life cycle, DNA, along with proteins, is a mass of loose strands called chromatin (KROH-muh-tin). Before cell divion, DNA is duplicated, or copied. Then, in an early stage of cell division, the chromatin is compacted into visible structures called chromosomes (KROH-muh-sohmz). A duplicated chromosomes consists of two identical structures called chromatid (KROH-muh-tidz). The chromatids are held together by a centromere (SEN-truh-mir).
Why is cell division important?
All living things are made up of cells. Many organisms start as one cell. The cell divides and becomes two cells, two cells become four, four become eight, and so on. Through the process of cell division, the organism grows. Cell division is still important after an organism stops growing. For example, every day billions of your red blood cells wear out and are replace through cell division. During the time it takes you to read this sentence, your bone marrow produced about six million red blood cells. Cell division is the way a one-celled organism, a unicellular organism, makes another organism of its kind. When a one-celled organisms reaches a certain size, it reproduces by dividing into two cells.
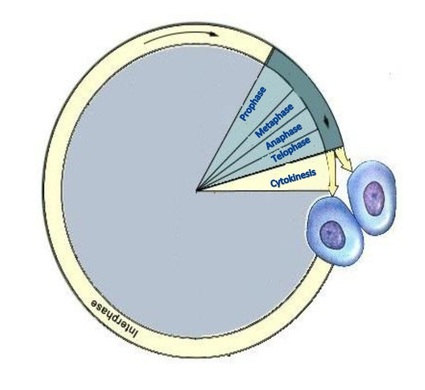
Interphase
The part of the cell cycle during which the cell is not dividing is called interphase (IN-ter-fayz). A lot of activity takes place in this stage of the cell's life. The cell grows to about twice the size it was when it was first produced. It also produces various organelles. The cell engages in normal life activities, such as transporting materials into the cell and getting of wastes.
Changes that occur during interphase prepare a cell for division. Before a cell can divide, DNA must be duplicated. This ensures that after cell division, each new cell gets an exact copy of the genetic material in the original cell.
Changes that occur during interphase prepare a cell for division. Before a cell can divide, DNA must be duplicated. This ensures that after cell division, each new cell gets an exact copy of the genetic material in the original cell.
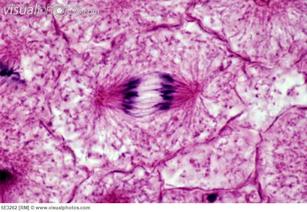
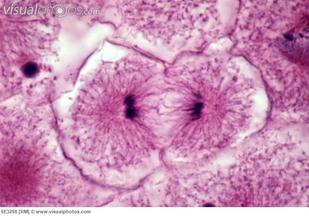
What are the phases of mitosis?
Mitosis has four phases: prophase (PROH-fayz), metaphase (MET-uh-fayz), anaphase (AN-uh-fayz), and telosphase (TEE-lo-fayz). I have heard telophase pronounced tel-o-phase, too.) By the end of these phases, the cell will have two identical nuclei and cytokinesis will begin.